To investigate the gender of the authors who publish articles of health economic evaluations in medicine and healthcare journals.
MethodWe evaluated a random sample of economic evaluations indexed in MEDLINE during 2019. Gender of the first, last and corresponding author was determined by review of the author's first name. Data were summarized as frequency and percentage for categorical items and median and interquartile range (IQR) for continuous items. We also calculated the index of authors per paper.
ResultsWe included 200 studies with 1365 authors (median of 6 authors per paper; IQR: 4-9). Gender identification was possible for all authors in the study sample: 802 (59%) were men and 563 (41%) were women. The number of female first, last, and corresponding authors respectively were 78 (39%), 68 (34%), and 80 (40%) for health economic evaluations.
DiscussionFemale scientists were underrepresented as co-authors and in prominent authorship positions in health economic evaluations. This study serves as a call to action for the scientific community to actively work towards equity and inclusion.
Investigar el género de las personas autoras que publican artículos de evaluaciones económicas de la salud en revistas de medicina y atención sanitaria.
MétodoSe evaluó una muestra aleatoria de evaluaciones económicas indexadas en MEDLINE durante 2019. El género de las personas autoras como primera, última y autoría de correspondencia se determinó mediante la revisión del nombre de la persona firmante. Los datos se resumieron como frecuencia y porcentaje para las variables categóricas, y como mediana y rango intercuartílico (RIC) para las variables continuas. También se calculó el índice de autores por artículo.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 200 estudios con 1365 autores (mediana de 6 autores por artículo; RIC: 4-9). La identificación del sexo fue posible para toda la muestra: 802 (59%) eran hombres y 563 (41%) eran mujeres. Los números de científicas con una posición como primera, última y autora de correspondencia fueron 78 (39%), 68 (34%) y 80 (40%), respectivamente, para las evaluaciones económicas.
DiscusiónLas científicas estuvieron infrarrepresentadas como coautoras y en puestos de autoría destacados en las evaluaciones económicas. Este estudio sirve como una llamada a la acción para que la comunidad científica trabaje activamente por la equidad y la inclusión.
Despite the significant contributions made by women in many scientific fields, a discernible underrepresentation exists in the authorship of pivotal research articles and publications.1–5 In a study of publications in The Lancet journals, only 32% and 23% of women were found to be first and last authors, respectively.6 A similar finding was observed in a study of high-impact, general medical journals, where women were found to represent only 34% of first authors in publications between 1994 to 2014.7
In the ever-evolving landscape of scientific research, the issue of gender disparity persists, casting a shadow over the equitable representation of female scientists in prominent authorship positions. However, to the best of our knowledge, no meta-research studies examining female authorship positions have been conducted within the realm of health economic evaluations. Health economic evaluations, which compare alternative interventions or programs in terms of their costs and outcomes, have been established as an important methodology for assessing value for money of healthcare interventions and can help inform decision making.
Here, we present a cross-sectional analysis of the gender of the authors who publish articles of health economic evaluations in medicine and healthcare journals. This study is ancillary to a broader meta-research project assessing practices that promote transparency, openness, and reproducibility in health economic evaluations.8
MethodWe used a database of health economic evaluations previously assembled, which consists of articles that were indexed in MEDLINE in 2019. A full description of the eligibility criteria and search strategy to identify these studies is available elsewhere8. Briefly, the database includes articles published in English reporting an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio in terms of costs per life years gained, quality-adjusted life years, and/or disability-adjusted life years. For each article, the number and gender of authors were extracted by two researchers (L.T.R., M.R. and/or F.C.L.) independently in duplicate. Gender of the first, last and corresponding author was determined by review of the author's first name. If an author's gender was unclear from their name, institutional websites and databases of literature (such as PubMed and Google) were reviewed to find photographs and/or biographical paragraphs. Gender identification databases were further referenced to confirm author's gender (e.g., https://gender-api.com/). Data were summarized as frequency and percentage for categorical items and median and interquartile range (IQR) for continuous items. We also calculated the index of authors per paper as the median number of authors per article considering only the different authors.
ResultsInclusion criteria led to 200 articles with 1365 authors (median of 6 authors per paper; IQR: 4-9). General characteristics of articles are presented in Table 1. Gender identification was possible for all authors in the study sample: 802 (59%) were men and 563 (41%) were women. Female scientists were underrepresented as co-authors (median of 2 female authors per paper; IQR: 1-4) and in prominent authorship positions in health economic evaluations. The numbers of female first, last, and corresponding authors, respectively, were 78 (39%), 68 (34%), and 80 (40%) for health economic evaluations (Table 2).
General characteristics of health economic evaluations.
| Characteristics | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Total number of articles | 200 (100%) |
| Journals containing three or more articles | |
| J Med Econ | 9 (5%) |
| PLoS One | 9 (5%) |
| Value Health | 7 (4%) |
| Appl Health Econ Health Policy | 4 (2%) |
| BMC Public Health | 4 (2%) |
| BMJ Open | 4 (2%) |
| Clin Ther | 3 (2%) |
| JAMA Netw Open | 3 (2%) |
| Vaccine | 3 (2%) |
| Other (journals with two or less articles) | 154 (77%) |
| Country of first author | |
| United States | 56 (28%) |
| United Kingdom | 28 (14%) |
| China | 17 (9%) |
| Canada | 15 (8%) |
| Australia | 10 (5%) |
| The Netherlands | 10 (5%) |
| Other | 64 (32%) |
| Type of condition addressed (ICD-10 category) | |
| Neoplasms (including cancers, carcinomas, tumors) | 55 (28%) |
| Infections and parasitic diseases | 37 (19%) |
| Diseases of the circulatory system | 21 (11%) |
| Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases | 12 (6%) |
| Other | 75 (38%) |
| Types of interventions addressed | |
| Nonpharmacological | 93 (47%) |
| Pharmacological | 84 (42%) |
| Both | 23 (12%) |
| Source of funding | |
| Non-profit | 116 (58%) |
| For-profit/mixed | 39 (20%) |
| Authors specified there was no funding | 45 (23%) |
| Conflicts of interest | |
| Authors declare no competing interests | 112 (56%) |
| Authors declare competing interests | 74 (37%) |
| Not reported/unclear | 14 (7%) |
ICD-10: International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision.
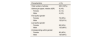
Description of authors’ (first, last, corresponding) gender.
| Characteristics | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Total number of articles | 200 (100%) |
| Authors per paper, median (IQR) | 6 (4-9) |
| Female | 2 (1-4) |
| Male | 4 (2-5) |
| First author gender | |
| Female | 78 (39%) |
| Male | 122 (61%) |
| Last author gender | |
| Female | 68 (34%) |
| Male | 132 (66%) |
| Corresponding author gender | |
| Female | 80 (40%) |
| Male | 120 (60%) |
IQR: interquartile range.
In this study, we investigated the gender of the authors who publish articles of health economic evaluations in medicine and healthcare journals. We found that female scientists were underrepresented as co-authors and in prominent authorship positions in health economic evaluations. Specifically, the number of female first, last, and corresponding authors respectively were only 39%, 34%, and 40%, respectively, for health economic evaluations. Overall, our findings are broadly in line with the previous studies of gender disparities in medical research.9–12 For the first time to our knowledge, we report inequities in authorship positions in health economic evaluations.
The observed underrepresentation of female scientists in prominent authorship positions within health economic evaluations, as revealed by our analysis, raises significant concerns about gender equity in the health economics and health services research community. These findings prompt a crucial discussion about the factors contributing to this underrepresentation and the potential implications for scientific progress and diversity within the field. One plausible explanation for the observed gender disparity could be the existence of systemic barriers that hinder the professional advancement of female scientists. These barriers may encompass implicit biases, unequal access to opportunities, and limited mentorship, all of which contribute to the lower participation and recognition of women in health economic evaluations. Additionally, the prevalence of gender stereotypes and preconceived notions about the roles of women in science may further impede their ascent to prominent authorship positions. Furthermore, it is essential to consider the potential impact of underrepresentation on the quality and breadth of research within health economic evaluations. A lack of diverse perspectives and experiences may result in a narrower range of research questions and methodologies, limiting the field's overall innovation and effectiveness.
The are some limitations to our analysis. We are unsure of the extent to which our findings generalize to health economic evaluations indexed outside of MEDLINE or health economic evaluations published in a language other than English. Similarly, only health economic evaluations of the medical and healthcare fields were included. Another possible limitation is that our cross-sectional analysis examined health economic evaluations that were published in 2019, before COVID-19 pandemic. Thus, it cannot be ruled out that different authorship estimates may be observed in a more current cross-section of health economic evaluations. Future (longitudinal) studies should examine gender trends of authorship positions in health economic evaluations.
ConclusionsAddressing the gender gap in health economic evaluations necessitates a multifaceted approach. Initiatives promoting gender diversity in leadership roles, such as mentorship programs, targeted outreach, and inclusive policies, can help create a more supportive environment for female scientists. Dismantling systemic barriers and promoting inclusivity will pave the way for more representative and impactful future in health economic research. This study provides baseline data to compare future progress in the field, but also serves as a call to action for the scientific community to actively work towards equity and inclusion, fostering a diverse and thriving landscape in health economic evaluations.
Availability of databases and material for replicationThe dataset will be freely available online in the Open Science Framework (osf.io/gzaxr), a secure online repository for research data.
Editor in chargePilar Pinilla Domínguez.
Despite the significant contributions made by women in many scientific fields, a discernible underrepresentation exists in the authorship of pivotal research articles and publications.
What does this study add to the literature?This study provides quantitative evidence of gender underrepresentation of female scientists as co-authors and in prominent authorship positions of health economic evaluations.
What are the implications of the results?Given this underrepresentation, it is imperative that the scientific community actively work towards promoting equity and inclusion when publishing in the field of health economic evaluations.
The corresponding author on behalf of the other authors guarantee the accuracy, transparency and honesty of the data and information contained in the study, that no relevant information has been omitted and that all discrepancies between authors have been adequately resolved and described.
Authorship contributionsL. Caulley, M. Ridao and F. Catalá-López contributed to conceptualizing and designing the study. F. Catalá-López supervised the study. L. Tejedor-Romero, M. Ridao and F. Catalá-López curated data. F. Catalá-López performed data analysis. L. Caulley and F. Catalá-López interpreted the study findings. L. Caulley and F. Catalá-López drafted the first version of the manuscript. L. Tejedor-Romero and M. Ridao commented for important intellectual content and made revisions. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
AcknowledgementsWe would like to express our sincere appreciation to Gift Anicho-Okereke for her invaluable assistance in editing and preparing this manuscript for submission.
FundingF. Catalá-López is supported by the Institute of Health Carlos III/CIBERSAM. L. Caulley is supported by the Lundbeck Foundation of Denmark. The views expressed in this manuscript are those of the authors and may not be understood or quoted as being made on behalf of, or reflection the position of, the funder(s) or any institution.
Conflicts of interestNone.