The 3rd International Nursing and Health Sciences Students and Health Care Professionals Conference (INHSP)
Más datosThis study aimed to assess risk of occupational safety and health in one of construction projects at Hasanuddin University.
MethodsThe research is a descriptive study with an observational approach. The sample in this study were all employees of Construction Projects in Hasanuddin University amounting 80 samples drawn using a purposive sampling method. The data analyzed using AS/NZS 4360 Risk Management Form.
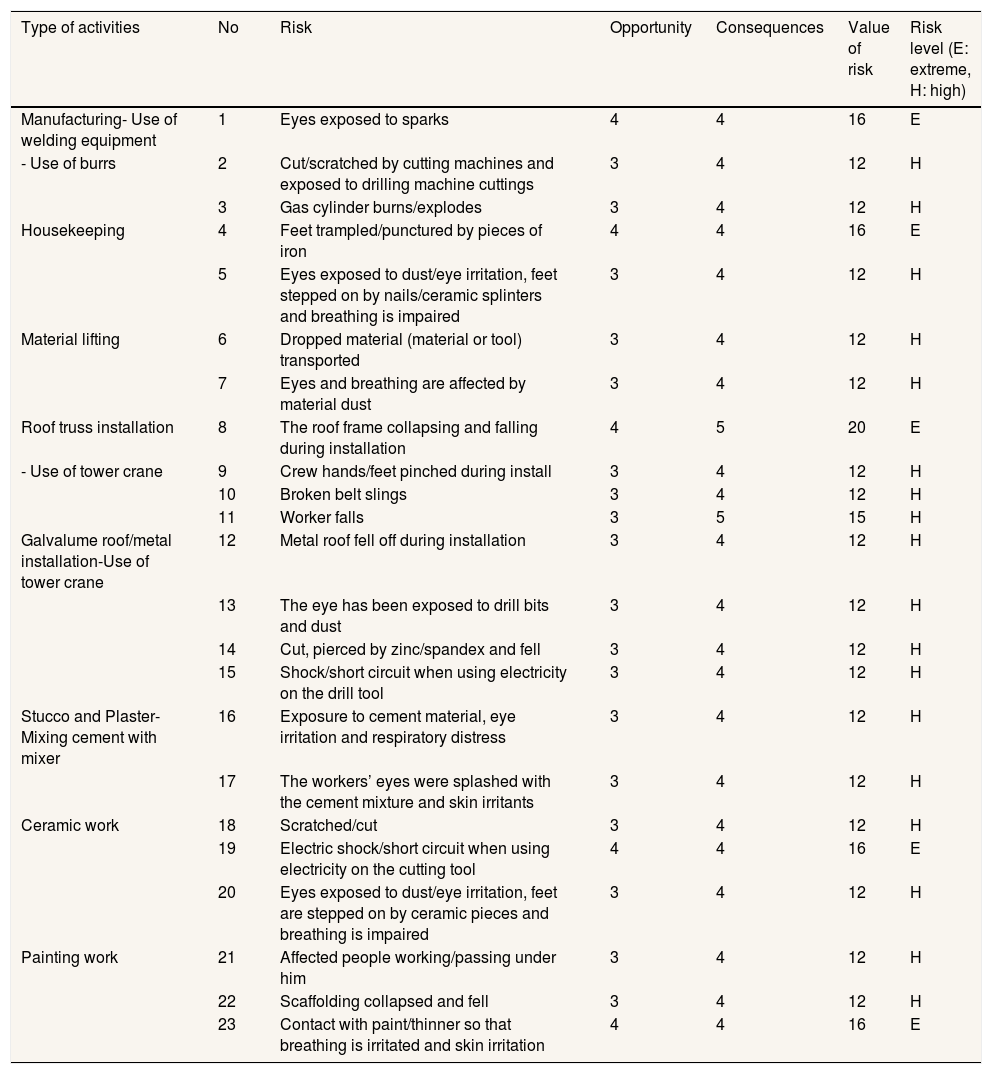
ResultIt was found that the types of activities that have an extreme level of risk are eyes exposed to sparks, feet being trampled or punctured by pieces of iron, electrocuted or shorted when using electricity in cutting tools, and exposed to paint or thinner so that breathing is disturbed and skin irritation with a value of each risk level 16. While the activities that have the highest extreme risk level with a risk level value of 20 are the roof frame collapsed and fell when installed.
ConclusionsThe highest risk is roof truss installation work with the risk of the roof frame collapsing and falling during the installation.
The construction process is a job that uses a lot of different tools, both automatic and manual. That tool is used in area in a lot of different types of job that can cause a high risk of occupational diseases and incidents. Equipment and machinery in an industry can cause dangers that are not only desired by humans but can also cause adverse health effects and interfere with work performance.1 In Nigeria for example, workers in many companies are exposed to many occupational hazards and air and water pollution control and waste and disposal management.2 A government safety register records 29,685 occupational accidents reported by companies in the Netherlands.3 Employees with occupations where they work with equipments have a five times increased risk in a work accident injury.4 Research conducted by Rahaded shows that the three highest risks, namely: dismantling the formwork column, there is a risk of worker falling with a risk of 7.92, service works and channels there is a risk of landslides digging with a risk index of 7.56, excavation work sloof there is a risk of landslides dug up with a risk index of 6.48.5 According to research conducted by Todingan concluded that there is a significant influence between the application the management of occupational safety and health with the cost of implementing construction projects.6 Simanjuntak's research shows that the OHS Management System can be applied in companies, as evidenced from the results of his research that the attitudes of all employees are in the support category towards the implementation of the OHS Management System and the actions of all employees are in the good category regarding the application of the OHS Management System.7 Other studies also concluded that all OSH Management System variables have a very strong correlation with work accident rates.8
The construction company is responsible for always giving the most excellent in each project development so that can be trusted to be a part of the growth of infrastructure in Indonesia to date by knowing the level of safety risks to workers. Because of the above cases, the researcher conducted research on safety risk assessment in one of the construction projects at Hasanuddin University.
MethodsThe research is a descriptive study with an observational approach. In this study, the research population used was all workers in one of the construction projects at Hasanuddin University, totaling 203 workers and 80 samples were drawn using a purposive sampling method. Having experience experiencing work accidents during the project. In the process of collecting data, researchers used a questionnaire to conduct interviews with informants. Data collection was carried out using questionnaires and interviews. Primary data is done by interviewing the questionnaire of the research subjects namely informants, and direct observation. Meanwhile, secondary data collection techniques were obtained from reviewing documents and other sources that could be used to support the research process. The data from this study were analyzed using SPSS and Excel programmes which are used to determine the level of safety risks of workers. Data analysis format is adjusted by risk measurement based on AS/NZS (Australian/New Zealand Standard) 4360 Risk Management which includes determining the context of activities to be managed risk, risk identification, risk analysis, and risk evaluation.
ResultThe types of risks that have extreme levels are eyes exposed to sparks, feet trampled/punctured by pieces of iron, roof frames collapse and fall during installation, shock/short circuit when using electricity in cutting tools, and are exposed to paint/thinner so that breathing irritated and irritated skin. The highest risk value was found in the type of roof truss installation with the risk of the roof frame collapsing and falling during the installation, which is a value of 20 (Table 1).
Risk identification results workers at construction in Hasanuddin University.
| Type of activities | No | Risk | Opportunity | Consequences | Value of risk | Risk level (E: extreme, H: high) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing- Use of welding equipment | 1 | Eyes exposed to sparks | 4 | 4 | 16 | E |
| - Use of burrs | 2 | Cut/scratched by cutting machines and exposed to drilling machine cuttings | 3 | 4 | 12 | H |
| 3 | Gas cylinder burns/explodes | 3 | 4 | 12 | H | |
| Housekeeping | 4 | Feet trampled/punctured by pieces of iron | 4 | 4 | 16 | E |
| 5 | Eyes exposed to dust/eye irritation, feet stepped on by nails/ceramic splinters and breathing is impaired | 3 | 4 | 12 | H | |
| Material lifting | 6 | Dropped material (material or tool) transported | 3 | 4 | 12 | H |
| 7 | Eyes and breathing are affected by material dust | 3 | 4 | 12 | H | |
| Roof truss installation | 8 | The roof frame collapsing and falling during installation | 4 | 5 | 20 | E |
| - Use of tower crane | 9 | Crew hands/feet pinched during install | 3 | 4 | 12 | H |
| 10 | Broken belt slings | 3 | 4 | 12 | H | |
| 11 | Worker falls | 3 | 5 | 15 | H | |
| Galvalume roof/metal installation-Use of tower crane | 12 | Metal roof fell off during installation | 3 | 4 | 12 | H |
| 13 | The eye has been exposed to drill bits and dust | 3 | 4 | 12 | H | |
| 14 | Cut, pierced by zinc/spandex and fell | 3 | 4 | 12 | H | |
| 15 | Shock/short circuit when using electricity on the drill tool | 3 | 4 | 12 | H | |
| Stucco and Plaster- Mixing cement with mixer | 16 | Exposure to cement material, eye irritation and respiratory distress | 3 | 4 | 12 | H |
| 17 | The workers’ eyes were splashed with the cement mixture and skin irritants | 3 | 4 | 12 | H | |
| Ceramic work | 18 | Scratched/cut | 3 | 4 | 12 | H |
| 19 | Electric shock/short circuit when using electricity on the cutting tool | 4 | 4 | 16 | E | |
| 20 | Eyes exposed to dust/eye irritation, feet are stepped on by ceramic pieces and breathing is impaired | 3 | 4 | 12 | H | |
| Painting work | 21 | Affected people working/passing under him | 3 | 4 | 12 | H |
| 22 | Scaffolding collapsed and fell | 3 | 4 | 12 | H | |
| 23 | Contact with paint/thinner so that breathing is irritated and skin irritation | 4 | 4 | 16 | E |
The work of installing or installing the roof truss is done using the Tower Crane tool. Workers who do this work at a height that must have a high level of concentration. Based on the results of research by Mayasari who conducted hazard identification and risk assessment on Tower Cranes, it was concluded that the danger of falling from a height was in the installation and dismantling work of Tower Cranes and when carrying out activities on these tools. This is due to workers being afraid of heights, inexperienced workers working at heights, workers not using body harness.9
Manullang also examines the risk assessment of work safety in the implementation of 20 high-rise building construction projects in Jakarta. Results obtained show that the biggest risk that occurs is the type of accident with the fall of people by 26.59%. Next in a row are falling objects, landslides, collapsing, getting hit/pinched, and being electrocuted by percentages of 18.73%, 16.46%, 15.33%, 14.64%, and 8.26%. Manuaba (1990) argued that excessive working hours, overtime hours beyond the ability limit will accelerate the appearance of fatigue, reduce speed, accuracy, and work accuracy.10 Päivi also revealed that the number of work-related accidents and fatal work-related diseases has increased, but the death rate per 100,000 workers has decreased. There were nearly 360,000 fatal occupational accidents in 2003 and nearly 2 million work-related illnesses that were fatal in 2002. Every day more than 960,000 workers are injured due to accidents. Every day 5330 people die from work-related diseases.11
The results of this risk identification produce 5 risks with extreme levels and 18 risks with high levels. This shows that workers assume all work done at this finishing stage has a high risk. There is no evidence of medium or low-risk work. Workers’ awareness is high enough about the work risks they face at any time. This is of course very supportive in doing work safely. This can also be used as a parameter for the success of the safety of this project personnel who have carried out various occupational safety and health programmes such as safety induction, sign making and installation for occupational safety and health and the environment, safety talk/safety morning talk, daily safety inspection for occupational safety and health and Environment, Safety Patrol, PPE Provision, Monthly Meeting Committee, Safety Award, Licensing/Legal, Training for Full Body Harness, and Occupational Safety and Health Programming and Environment, HIRARC and JSA. The Occupational Safety and Health Programming can increase the knowledge of employee. A study shows that there is an effect education and knowledge can positively reduce injury.12
A research conducted in the same place with this research showed that the Occupational Safety and Health programme cost investment in construction project is categorized as beneficial for the company.13 Research conducted by Aulia, the results of interviews with OHS experts regarding the amount of work accident penalties for construction workers concluded that the penalty for serious accidents without death is IDR 100–250 million and the amount of penalty for accidents in the form of death is IDR 250–500 million.14 All potential hazards have been controlled and meet safety standard limits, thus contributing to the creation of a safe, healthy work environment and smooth production processes, which in turn can reduce the risk of loss and have an impact on increasing company productivity. Companies that can manage risk well are seen as having a sensitive ability to detect risk, have the flexibility to respond to risks and guarantee the capability of resources to take action to reduce the level of risk, while those that are unable to manage risk properly will cause a waste of resources and time and not achieving company goals.15
The benefits of risk management are ensuring business continuity by reducing the risk of any hazardous activity, reducing costs for handling unwanted events, creating a sense of security among shareholders regarding the sustainability and safety of their investments, increasing understanding and awareness of operational risks for each element in the organization/company, and meet the requirements of the applicable laws.16
ConclusionThis study has 23 construction activities that have risks analyzed to find the risk value and risk level. The results found were that 5 construction activities had the highest value of risk and extreme risk level with one of them being the highest among the 5 being the roof frame collapsing and falling during installation activities with a value of risk of 20 and an extreme risk level.
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
Peer-review under responsibility of the scientific committee of the 3rd International Nursing, Health Science Students & Health Care Professionals Conference. Full-text and the content of it is under responsibility of authors of the article.